Arthritis is a condition that affects the joints and frequently develops as people get older. In reality, practically all of us are familiar with someone who has arthritis.
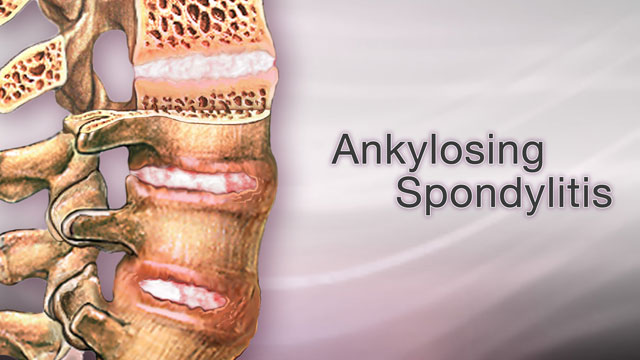
There are various forms of arthritis today. Arthritis that affects the spine is called ankylosing spondylitis. The spinal cord’s bones merge in this disease. The spine becomes less flexible as a result, which causes pain.
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that predominantly affects the spine, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In this blog post, we will explore the ins and outs of ankylosing spondylitis, from recognizing its symptoms to discussing effective treatments.
Let’s take a closer look at this condition and the steps to living a better life with it.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a type of arthritis that primarily targets the spine, causing inflammation of the spinal joints and ligaments. Over time, this inflammation can lead to the formation of new bone, causing the vertebrae to fuse together. Here are some key points to understand about AS:
Symptoms Develop Gradually:
Ankylosing spondylitis symptoms typically emerge gradually, making it challenging to diagnose in its early stages.
Affects More Than Just the Spine:
While the spine is the primary target, ankylosing spondylitis can also affect other parts of the body, including the hips, shoulders, and even the eyes.
No Known Cure:
AS is a lifelong condition, but with the right management, it can be effectively controlled to minimize pain and stiffness.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of AS is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Common symptoms include:
- Back Pain: Persistent lower back pain is often the first sign of AS. The pain is typically worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the lower back and hips can be a significant symptom. People with AS may find it difficult to bend or twist.
- Fatigue: Chronic pain and inflammation can lead to fatigue, impacting daily life.
- Loss of Mobility: As the condition progresses, AS can reduce spinal flexibility, leading to limited mobility.
- Eye Inflammation: AS can cause inflammation in the eyes, leading to redness, pain, and sensitivity to light.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment
While there’s no cure for AS, several treatment options are available to manage the condition effectively:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics may also be recommended.
- Physical Therapy: Regular exercise and physical therapy can help maintain flexibility, improve posture, and manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Proper posture, ergonomic workspaces, and regular stretching can help manage the symptoms of AS.
- Surgery: In severe cases where joint damage or deformity occurs, surgical intervention may be necessary.
- Patient Support: Joining a support group or working with a counselor can provide emotional and mental support for coping with the challenges of AS.
Living with Ankylosing Spondylitis can be challenging, but it’s important to remember that there are effective treatments and strategies to manage the condition.
Early diagnosis, symptom recognition, and a tailored treatment plan can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis.
If you suspect you may have AS or are struggling with its symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and guidance on managing your condition.
Treating Ankylosing Spondylitis with Biological Infusion Therapy
Biological infusion therapy has proven to be a valuable and effective treatment option for ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the spine, leading to pain, stiffness, and inflammation.
Biological infusion therapy, a form of targeted therapy, can help individuals with AS by specifically addressing the underlying causes of the condition. Here’s how it helps in treating AS:
Targeted Approach:
Biological infusion therapies are designed to target specific molecules or cells in the immune system responsible for inflammation. In the case of AS, these therapies often focus on blocking a molecule called tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). TNF-alpha is known to play a significant role in causing inflammation in the joints and spine in AS patients.
Reducing Inflammation:
By blocking TNF-alpha and other inflammatory pathways, biological infusion therapy can significantly reduce inflammation in the spine, joints, and other affected areas. This reduction in inflammation helps alleviate the pain, stiffness, and discomfort associated with AS.
Slowing Disease Progression:
One of the primary goals of biological infusion therapy is to slow down the progression of AS. Over time, AS can lead to structural damage and fusion of the spinal vertebrae. Biological therapy has been shown to prevent or delay this fusion, helping patients maintain mobility and flexibility.
Pain Relief:
By reducing inflammation and preventing further structural damage, biological infusion therapy can provide pain relief for AS patients. This improvement in pain management allows individuals to lead more active and comfortable lives.
Improved Functionality:
Ankylosing spondylitis can lead to significant limitations in mobility and function. Biological therapy can help restore or maintain joint and spinal mobility, allowing individuals to perform daily activities with greater ease.
Long-lasting Effects:
Biological infusion therapy typically provides long-lasting results. Patients may require infusions at regular intervals, but the treatment’s impact on symptoms and disease progression can persist between infusions.
Personalized Treatment:
Healthcare professionals can tailor biological infusion therapy to the specific needs of each ankylosing spondylitis patient. This personalized approach takes into consideration factors such as the patient’s medical history, ankylosing spondylitis severity, and response to treatment.
It’s important to note that while biological infusion therapy is a promising treatment option for AS, it is not a cure. Ankylosing spondylitis is a lifelong condition, and treatment often involves a combination of therapies, including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Decisions regarding the use of biological infusion therapy should be made in consultation with a rheumatologist or another medical specialist experienced in treating AS.
Ultimately, the goal of biologic infusion therapy in ankylosing spondylitis treatment is to improve the patient’s quality of life by reducing pain, inflammation, and disease progression while promoting better mobility and function.
Fuse Infusion Helps You in Treating Ankylosing Spondylitis
If your doctor has recommended biological therapy treatment for ankylosing spondylitis, we at Fuse Infusion offer you the best treatment services. We treat ankylosing spondylitis through medications, which are specialized biologics, and help our patients in overcoming this chronic disease.
Each Fuse Infusion patient receives direct care and treatment from our licensed professionals throughout biological infusion therapy, providing thorough medical management.
From start to end, each patient receives individualized care. When required, on-call medical professionals are accessible.
At Fuse Infusion, we believe in offering premium-quality services to our patients. So, contact us to receive a biological infusion today!